Blockchain technology has paved the way for secure, transparent, and decentralized systems that operate independently of centralized control. However, scalability and transaction throughput have been significant obstacles for early blockchain systems. Layer 1 protocols, which form the foundation of the blockchain ecosystem and are responsible for ledger maintenance, network security, and transaction processing, aim to address these issues.
In recent times, several Layer 1 protocols have emerged, each boasting unique features to tackle the limitations of previous blockchains. Solana, for instance, has captured attention due to its remarkable capacity to handle over 65,000 transactions per second, making it one of the fastest Layer 1 protocols. This article offers an insightful introduction to Layer 1 protocols, focusing especially on the promising capabilities of Solana and its competitors. We will dive into their distinctive features, compare their performance, and explore their potential applications within the blockchain ecosystem.
What Are Layer 1 Protocols?
Layer 1 protocols serve as the foundation for the entire blockchain ecosystem, providing the framework for secure, decentralized, and transparent transactions. They function as the base layer for all operations within the blockchain, ensuring stability and consistency across the network.
One of the key features of Layer 1 protocols is the maintenance of the blockchain's transaction ledger. This is accomplished through a consensus mechanism that guarantees agreement among all network nodes on the blockchain's state. This aspect of Layer 1 protocols safeguards the security and immutability of the blockchain, protecting it from potential tampering or manipulation.
Another vital role of Layer 1 protocols is transaction processing. This encompasses verification of transaction validity, appending them to the ledger, and updating the blockchain's state accordingly. Efficient transaction processing is crucial for the seamless functioning of decentralized applications (dApps) built on the blockchain, as it assures that transactions are carried out securely and effectively.
Additionally, Layer 1 protocols supply the infrastructure needed for smart contract functionality. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that automatically execute when specific conditions are met. These contracts play a significant role in various dApps and are employed for diverse purposes, such as decentralized finance (DeFi), gaming, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Solana vs. Other Layer 1 Protocols
When comparing Solana with other Layer 1 protocols, it's essential to assess their respective features, abilities, and performance. The following points highlight Solana's comparison with various other Layer 1 protocols:
- Ethereum: The most used Layer 1 protocol for decentralized applications development, Ethereum has a considerably lower transaction processing rate (TPS) than Solana, at around 2-20 TPS, although this is likely to increase in the future with the adoption of Layer 2 solutions and the EIP 4844 upgrade.
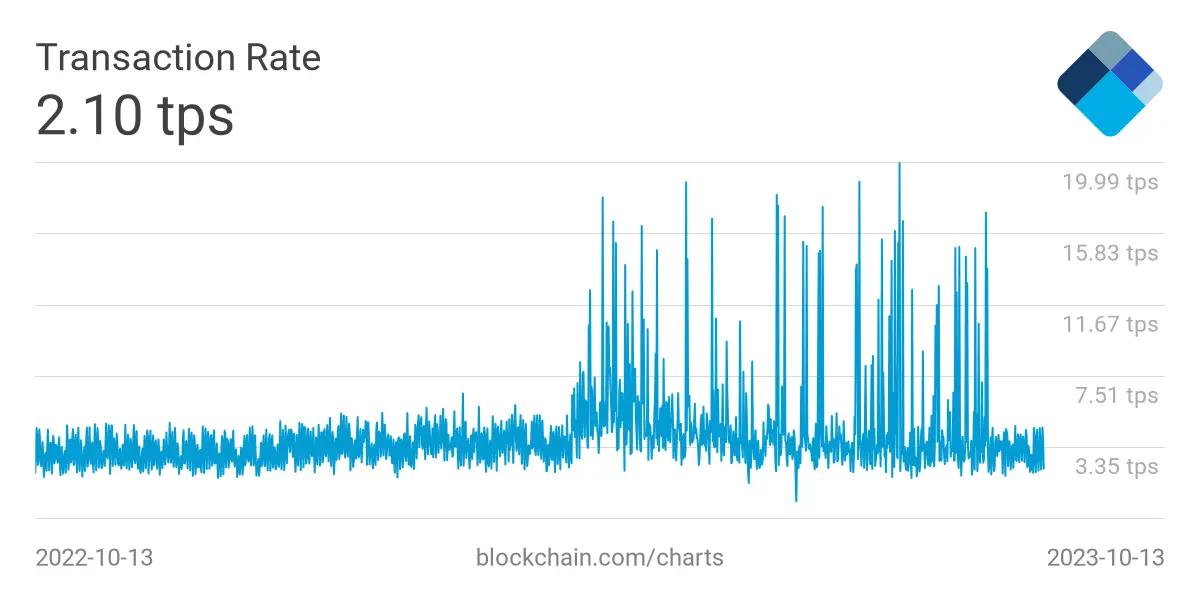
- Bitcoin: As the pioneer Layer 1 protocol, Bitcoin mainly functions as a store of value and a medium of exchange. However, its TPS is significantly lower than Solana's, with around 7 TPS.
- Polkadot: This Layer 1 protocol aims to facilitate interoperability among different blockchains. Although Polkadot's TPS is higher than Ethereum's, it still falls short of Solana's processing rate. Polkadot uses a hybrid consensus mechanism combining proof-of-stake and nominated proof-of-stake, which contrasts with Solana's proof-of-stake mechanism.
- Cosmos: Like Polkadot, Cosmos is designed as a Layer 1 protocol that promotes interoperability between blockchains. While its TPS is higher than Ethereum's, it remains lower than Solana's processing capabilities. Cosmos adopts the Tendermint consensus mechanism, differing from Solana's proof-of-stake approach.
As a Layer 1 protocol, Solana excels in processing a large number of transactions per second while maintaining decentralization and security. Though other Layer 1 protocols offer unique features and capabilities, Solana's TPS is unmatched in the blockchain ecosystem, positioning it as a competitive platform for building high-performance decentralized applications.
Overview of Solana
Solana, as a Layer 1 protocol, was developed to tackle the scalability and performance challenges faced by earlier blockchain systems. Founded by former Qualcomm software engineer Anatoly Yakovenko, it has been in operation since March 2020. A key attribute of Solana is its capacity to handle a vast number of transactions per second (TPS), currently exceeding 65,000 TPS.
This impressive performance is a result of groundbreaking technologies, including Tower BFT, a unique proof-of-stake consensus mechanism that uses a verifiable delay function (VDF) to safeguard against network attacks and speed up block propagation. The network performance is further optimized through Solana's dynamic validators and archivers.
Offering modularity and flexibility, Solana's architecture enables seamless integration with other blockchain systems and technologies. The platform also features Saber, an intelligent contract language similar to Ethereum's Solidity, facilitating the development of decentralized applications (dApps) on Solana.
Also, one of Solana's major advantages is its low transaction fees, averaging around $0.0001 per transaction. This makes the platform ideal for creating high-performance, low-cost dApps in industries such as decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and gaming.
Solana has garnered substantial attention from the blockchain community and attracted investments from notable entities like Andreessen Horowitz, Polychain Capital, and Alameda Research. Moreover, it has been integrated with numerous blockchain systems and projects, such as Serum (a decentralized exchange), Mango Markets (a decentralized trading platform), and Chainlink (a decentralized oracle network).
How Solana Functions
Proof-of-Stake Mechanism
Solana employs a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus method named Tower BFT, which is built for high scalability and energy efficiency. Tower BFT uses a verifiable delay function (VDF) to mitigate network attacks and enable quicker block propagation. The system also incorporates dynamic validators and archivers to enhance network performance.
Efficient Transaction Handling
Solana is engineered to manage a substantial volume of transactions per second (TPS), currently surpassing 65,000 TPS. This is accomplished through parallel processing, which allows for concurrent transaction processing, and streaming data structures, which reduce transaction processing time.
Adaptable Structure
The architecture of Solana is designed for modularity and adaptability, supporting seamless integrations with other blockchain systems and technologies. Its component-based approach ensures that each component is highly optimized and specialized for a particular function.
Solana's Transactional Layer: Saber
The platform features an inbuilt smart contract language called Saber, similar to Ethereum's Solidity, which enables the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) on Solana. Saber is intended to be high-performance, secure, and user-friendly.
Minimal Transaction Costs
Average transaction fees on Solana are approximately $0.0001 per transaction, making it a favorable platform for developing high-performance, cost-effective dApps.
Solana aims to overcome the scalability and performance constraints of earlier blockchain systems while preserving decentralization and security. Its modular, flexible, and optimized design positions it as a promising platform for building high-performance, decentralized applications that can scale with the growing blockchain ecosystem.
Other Layer 1 Protocols
Polkadot
Polkadot is a cutting-edge blockchain protocol aimed at facilitating interoperability between various blockchain systems. By utilizing a sharding architecture, it enhances scalability and includes an embedded governance system that empowers token holders to vote on protocol updates.
Avalanche
Avalanche is a high-performance blockchain protocol designed to achieve rapid transaction finality and accommodate millions of validators. It employs a consensus mechanism known as Avalanche-X, which is engineered to be both highly efficient and secure.
Cosmos
Cosmos is a decentralized network comprised of autonomous blockchains connected through a hub-and-spoke model. It encompasses an inherent governance system that enables token holders to vote on protocol modifications and supports the creation of custom blockchains.
Near Protocol
Focused on speed, scalability, and developer-friendliness, Near Protocol is a blockchain protocol that employs a consensus mechanism called Nightshade, designed for efficiency and security. Additionally, it features an integrated smart contract language dubbed AssemblyScript.
Aptos
Aptos is one of the more recent Layer 1 blockchains to launch, which is built using the Move programming language and was founded by engineers who worked on Facebook's Diem project. Aptos promises higher throughput and enhanced security than its counterparts.
Solana Use Cases
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Due to its rapid and efficient transaction processing abilities, Solana is well-suited for DeFi applications, such as:
- Decentralized exchanges
- Lending and borrowing platforms
- Asset management tools
This enables smooth crypto trading and secure finance operations in a decentralized environment.
Gaming
Solana provides the performance and scalability required for gaming applications that can handle:
- High-speed gameplay
- A large number of users and transactions
Blockchain gaming platforms benefit from these features, ensuring an immersive and enjoyable gaming experience.
Supply Chain Management
Using Solana for blockchain-based supply chain management solutions helps:
- Track goods and materials throughout the supply chain
- Maintain transparency and immutability
These attributes ensure a secure and efficient process, enhancing trust among parties involved.
Identity Management
Solana enables the development of secure identity management solutions, allowing users to:
- Manage digital identities
- Control access to personal data
This ensures enhanced privacy and security for online transactions and verifications.
Social Media
Decentralized social media platforms using Solana can:
- Provide better security and privacy features
- Offer users more control over personal data and content
These aspects encourage a more user-centric approach to online communication, avoiding potential data abuses.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Solana's scalability and security features make it ideal for IoT applications:
- Connected devices requiring secure data transfer
- Efficient communication between multiple devices
This promotes seamless integration of IoT devices in various environments, providing improved connectivity and efficiency.
TL;DR
Solana is a Layer 1 blockchain known for high-speed transactions (over 65,000 TPS). Developed by Anatoly Yakovenko, it surpasses competitors like Ethereum and Bitcoin in transaction speeds and offers low fees ($0.0001 per transaction). Solana's unique features, such as Tower BFT for consensus and Saber for smart contracts, make it ideal for various applications, from DeFi and gaming to supply chain and IoT.











