Ethereum, as one of the pioneers of blockchain technology, revolutionized the way we perceive decentralized applications and smart contracts. However, as the Ethereum network gained popularity, it started facing significant scalability issues. With a limited capacity of around 30 transactions per second (TPS), Ethereum's network often becomes congested during periods of high demand, leading to slow transaction speeds and exorbitantly high gas fees. These issues make it a challenging environment for developers and users alike, and they highlight the urgent need for a scalability solution to accommodate the increasing demands on the network.
Layer 2 Solutions
To overcome these challenges, developers have been working on various Layer 2 (L2) scaling solutions. Layer 2 solutions are protocols that operate on top of the Ethereum blockchain (Layer 1), aiming to significantly increase transaction throughput, decrease latency, and reduce transaction costs. These L2 solutions use various blockchain technology such as sidechains and rollups to achieve faster and more cost-effective transactions. They allow for most transactions to be processed off-chain, while still maintaining the security and decentralization of the main Ethereum blockchain. Popular L2s include Optimistic Rollups, zk-Rollups, and sidechains like Polygon.
Introduction to Mantle Network
Enter Mantle Network, a promising and ambitious Layer 2 scaling solution designed for the Ethereum blockchain. Mantle Network is built to be an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible Layer-2 solution that leverages Optimistic Rollups technology. This design allows for fast and cheap transactions by bundling multiple transactions off-chain and then submitting them as a single batch to the Ethereum main chain for final settlement. It’s an ingenious workaround that aims to significantly reduce the congestion on the Ethereum network, while also drastically lowering the cost of executing smart contracts and conducting transactions.
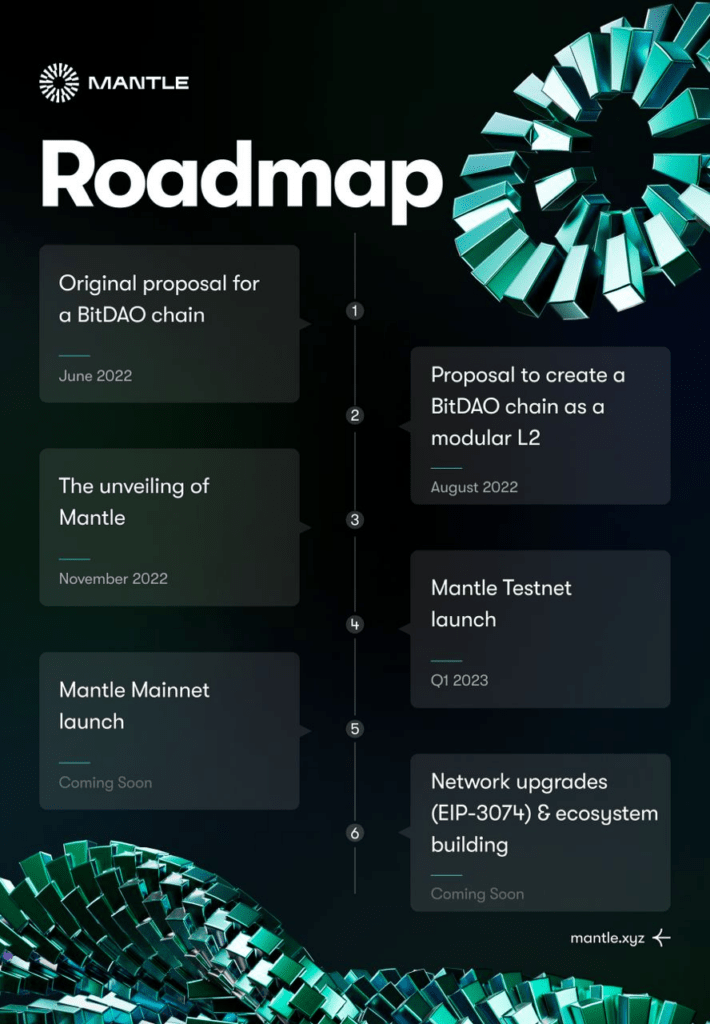
A defining moment in Mantle Network's journey came in May 2023 when it merged with BitDAO, one of the most well-funded decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) in the crypto space. BitDAO was established by the co-founders of the renowned centralized exchange Bybit, Daniel Yan and Ben Zhou, in June 2021. This merger was more than just a partnership; it effectively combined two powerful entities into a singular, unified ecosystem under one brand and token: Mantle (MNT). This merger provided Mantle Network with a remarkable treasury, valued at over $3 billion at the time of the merger, and a $200 million ecosystem fund dedicated to supporting early-stage DApps development on Mantle. With this substantial backing, Mantle Network is not just another Layer 2 solution; it is poised to be a major player in the Ethereum scaling arena.
How Mantle Network Works
Mantle Network is designed as a modular system, allowing components of the network to be developed, updated, and replaced independently of each other. This architecture promotes flexibility, making it easier for Mantle to adapt to technological advancements and changing user demands over time. It stands in contrast to more rigid, monolithic blockchains where changes can be complex and risky to implement.
Optimistic Rollups and EigenDA Technology
At the core of Mantle Network is its use of Optimistic Rollups, a Layer 2 scaling solution that executes transactions off-chain while maintaining the security of the Ethereum mainnet. Optimistic Rollups rely on a system where transactions are grouped together into a single batch, which is then cryptographically hashed and recorded on the mainnet. In tandem with Optimistic Rollups, Mantle employs its proprietary EigenDA technology, designed to enhance data availability and network performance. EigenDA allows Mantle to ensure that off-chain data remains available, secure, and tamper-proof.
Comparison with Monolithic Blockchains
In contrast to monolithic blockchain technology, which is rigid and can be slow to adapt to new technological developments, Mantle Network’s modular design enables rapid iteration and upgrades. The adoption of Optimistic Rollups and EigenDA also sets Mantle Network apart, providing enhanced scalability, speed, and data availability that many monolithic blockchains struggle to achieve.
Network Participants
Sequencers
Sequencers are special nodes in the Mantle Network that order transactions into a sequence. This ordered list of transactions is then processed and batched into a rollup, which is ultimately submitted to the Ethereum mainnet.
Rollup Verifiers
Rollup verifiers are nodes responsible for verifying rollups submitted by the sequencers. They play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity and security of transactions processed off-chain.
DA Nodes
Data Availability (DA) Nodes store and serve the off-chain data required for reconstructing the rollup state. They are vital to Mantle's EigenDA technology, ensuring that data remains accessible and secure.
TSS Nodes
Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) Nodes contribute to the network's security by collaboratively generating and securing cryptographic signatures, which are essential for validating transactions and maintaining integrity within the network.
Transaction Lifecycle
Initiation
A user initiates a transaction by sending it to a sequencer.
Handling
The sequencer organizes transactions into a queue, batches them together, and then sends this batch as a single rollup to the Ethereum mainnet.
Storage
The corresponding data of the transaction, necessary for validation and state reconstruction, is stored by the DA Nodes, making it available for verification and future access.
Bridging to Other Networks
Mantle Network is designed to be interoperable, allowing for seamless interactions with other blockchain networks. Through specialized bridge contracts, assets and data can move bi-directionally between Mantle and other chains, making it a powerful tool for cross-chain applications and services.
Governance Structure of Mantle
Mantle Network adopts a decentralized governance model, empowering its community of token holders to propose, debate, and vote on changes to the network. This approach ensures that the direction and evolution of Mantle are determined by those who use and have a stake in the network, aligning the interests of developers, users, and stakeholders.
The EigenLayer
The EigenLayer is a cornerstone technology within the Mantle Network. It is a sophisticated data availability layer designed to ensure that off-chain data processed in the Optimistic Rollups remains accessible, secure, and tamper-proof. Unlike conventional L2s EigenLayer enhances Mantle's scalability without sacrificing the strong security guarantees provided by the Ethereum mainnet.
How it Empowers Mantle's Data Availability Layer
One of the critical challenges in scaling blockchain technology is maintaining data availability, i.e., ensuring that all necessary data to reconstruct the blockchain's state is readily available when needed. Mantle’s EigenLayer solves this problem by creating a robust and decentralized data availability layer. Here is how it empowers Mantle:
Decentralization: The EigenLayer is designed as a network of nodes that independently validate and store off-chain data, reducing the reliance on centralized parties.
Efficiency: By using advanced data encoding and storage techniques, EigenLayer optimizes the throughput of the network and reduces the costs associated with data storage and retrieval.
Interoperability: The EigenLayer is not just tied to Mantle; it is designed to be a versatile layer that can be employed by other L2s, enabling broader ecosystem compatibility.
The Role and Utilities of MNT
The MNT token is the native utility token of the Mantle Network. It plays a central role in the ecosystem, designed to incentivize and facilitate various operations and governance within the network. Here are some of its primary roles and utilities:
Governance: MNT token holders have the power to propose and vote on key decisions regarding the network’s development, changes in parameters, and adoption of new features.
Staking: Users can stake MNT tokens to participate in the network’s consensus, thereby helping to secure the network and, in return, earning staking rewards.
Payment for Services: MNT is used to pay for transaction fees and other services within the Mantle Network. This ensures the token has intrinsic value as the fuel for network operations.
Liquidity Provision: MNT can be used to provide liquidity in various decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, enabling additional utility and rewards for holders.
Mantle Network vs. Other L2s
In a landscape where Layer 2 (L2) solutions are emerging as pivotal tools for scaling Ethereum and other blockchain networks, it’s crucial to understand where Mantle Network stands relative to other L2 platforms.
Mantle Network is designed for high throughput and low latency, potentially outpacing other L2 solutions in transactions per second (TPS). While many L2 solutions focus on scalability, they may compromise on decentralization or security; Mantle aims for a balance among these key attributes.
Fees and Costs: Mantle Network has been developed with the aim of significantly reducing transaction fees. Its unique architecture might allow for lower costs compared to other L2 solutions.
Ease of Use and Developer Experience: Mantle Network might provide more straightforward and developer-friendly tools and APIs compared to some other L2 solutions, thereby lowering the entry barrier for developers.
Modular Design: Mantle Network’s modular design stands out as a major differentiator. It allows components of the network to be upgraded and modified without disrupting the entire system, promoting flexibility and future-proofing the protocol.
EigenLayer Technology: Mantle’s EigenLayer is a core innovation, empowering its data availability layer and possibly setting it apart from other L2 solutions that might not have a comparable feature.
Native Token Utilities and Ecosystem: The MNT token is more than just a gas payment mechanism; it plays a multifaceted role in governance, staking, and ecosystem incentives, possibly offering broader utility than tokens in other L2 solutions.
Merger with BitDAO: The merger with BitDAO is a strategic move that potentially brings unprecedented capital and resource backing to Mantle Network, setting it apart from other L2 solutions.
Holistic Approach to Scalability, Security, and Decentralization: Mantle Network might aim for a unique balance among scalability, security, and decentralization, avoiding the pitfalls of focusing too heavily on just one of these critical aspects.
The Challenges Facing Mantle Network
Adoption and Recognition: As a new entrant in the crowded Layer 2 space, Mantle Network needs to gain significant traction among developers, users, and enterprise adopters to secure its place in the market.
Competitive Landscape: The L2 solutions market is highly competitive, with numerous well-established players. Mantle Network must differentiate itself effectively and sustainably to succeed.
Unproven Long-Term Viability: As a newcomer, Mantle's long-term viability and resilience under various network conditions and attack vectors remain to be seen.











